Effective weed control is a crucial aspect of agricultural management, and mesotrione is a widely used herbicide for this purpose. However, optimizing its application rates is essential to ensure maximum efficacy while minimizing environmental impact and cost. In this article, we will delve into the world of mesotrione application rates, exploring the factors that influence its effectiveness and providing guidance on how to optimize its use.
Understanding Mesotrione
Mesotrione is a triketone herbicide that inhibits the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD), which is essential for the biosynthesis of carotenoids in plants. By blocking this enzyme, mesotrione prevents the production of carotenoids, leading to the death of sensitive plant species. It is commonly used for pre-emergence and post-emergence control of broadleaf weeds in corn and other crops.

Factors Affecting Mesotrione Efficacy
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of mesotrione, including:
- Application rate: The amount of mesotrione applied per unit area can significantly impact its efficacy.
- Weed species: Different weed species have varying levels of susceptibility to mesotrione.
- Growth stage: The growth stage of the weeds at the time of application can affect the efficacy of mesotrione.
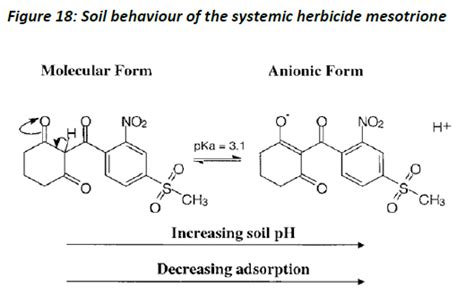
- Soil type: The type of soil can influence the availability and activity of mesotrione.
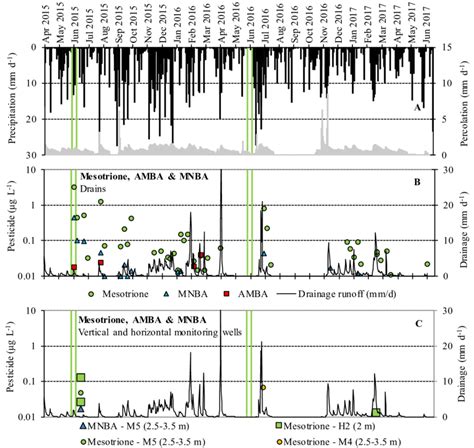
- Environmental conditions: Weather conditions, such as temperature and rainfall, can impact the efficacy of mesotrione.
Optimizing Mesotrione Application Rates
To optimize mesotrione application rates, it is essential to consider the factors mentioned above. Here are some guidelines to help you get the most out of your mesotrione application:
- Use the recommended rate: Always follow the recommended application rate for mesotrione, as specified on the product label.
- Adjust for weed species: Adjust the application rate based on the type of weeds you are trying to control. For example, some weeds may require a higher rate of mesotrione for effective control.
- Consider the growth stage: Apply mesotrione at the optimal growth stage for the weeds you are trying to control. For example, applying mesotrione to weeds in the seedling stage can be more effective than applying it to mature weeds.
- Take into account soil type: Adjust the application rate based on the type of soil you are working with. For example, mesotrione may be more effective in sandy soils than in clay soils.
Benefits of Optimizing Mesotrione Application Rates
Optimizing mesotrione application rates can have several benefits, including:
- Improved efficacy: By applying the optimal rate of mesotrione, you can achieve better weed control and reduce the risk of weed resistance.
- Reduced environmental impact: By using the minimum effective rate of mesotrione, you can reduce the amount of herbicide released into the environment.
- Cost savings: Optimizing mesotrione application rates can help reduce the overall cost of weed control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing mesotrione application rates is crucial for effective weed control while minimizing environmental impact and cost. By considering the factors that influence mesotrione efficacy and adjusting the application rate accordingly, you can achieve better weed control and reduce the risk of weed resistance. Remember to always follow the recommended application rate and take into account the specific conditions of your field to get the most out of your mesotrione application.



What is the recommended application rate for mesotrione?
+The recommended application rate for mesotrione varies depending on the specific product and the type of weeds being controlled. Always follow the recommended application rate specified on the product label.
How does soil type affect the efficacy of mesotrione?
+Soil type can affect the availability and activity of mesotrione. For example, mesotrione may be more effective in sandy soils than in clay soils.
What are the benefits of optimizing mesotrione application rates?
+Optimizing mesotrione application rates can improve efficacy, reduce environmental impact, and save costs.
