Welding is a vital process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion. This process has numerous applications across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and repair. One of the most comprehensive resources for understanding welding principles and applications is the "Welding Principles and Applications" textbook, now in its 8th edition.
Understanding Welding Processes
Welding involves several processes, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common welding processes include Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), and Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW). Each process has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of process depends on the type of material being welded, the thickness of the material, and the desired quality of the weld.
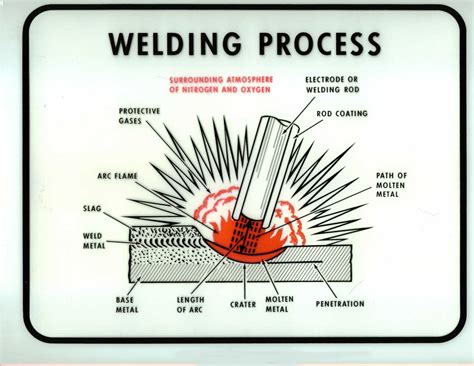
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
SMAW, also known as "stick" welding, is one of the most common welding processes. It uses a consumable electrode covered in a flux to protect the arc and molten metal from the atmosphere. SMAW is commonly used for welding steel, but it can also be used for welding other metals.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
GMAW, also known as "MIG" welding, uses a continuous wire electrode and an inert gas to shield the arc. This process is commonly used for welding thin metals, such as aluminum and steel. GMAW is a high-speed process that produces a clean and smooth weld.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
GTAW, also known as "TIG" welding, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas to shield the arc. This process is commonly used for welding thin metals, such as aluminum and stainless steel. GTAW produces a high-quality weld, but it is a slower process than GMAW.
Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
FCAW uses a special electrode that produces a flux to shield the arc. This process is commonly used for welding thick metals, such as steel. FCAW is a high-speed process that produces a strong and durable weld.

Welding Applications
Welding has numerous applications across various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
Construction
Welding is widely used in the construction industry for building bridges, ships, and buildings. Welding is used to join steel beams and other metal components to create the framework of a structure.
Manufacturing
Welding is used in the manufacturing industry to produce a wide range of products, including cars, trucks, and machinery. Welding is used to join metal components together to create the final product.
Repair
Welding is used in the repair industry to fix broken or damaged metal components. Welding can be used to repair cars, trucks, and machinery, as well as other metal objects.

Welding Safety
Welding can be a hazardous process if proper safety precautions are not taken. Some of the most common hazards associated with welding include:
Electric Shock
Welding involves the use of electrical current, which can cause electric shock if proper safety precautions are not taken.
Fire and Explosion
Welding involves the use of high heat, which can cause fires and explosions if proper safety precautions are not taken.
Eye and Skin Damage
Welding can cause eye and skin damage if proper safety precautions are not taken. Welders should wear protective gear, including helmets and gloves, to prevent injury.


Gallery of Welding Principles and Applications
What is welding?
+Welding is a process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion.
What are the most common welding processes?
+The most common welding processes include Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), and Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
What are the most common applications of welding?
+Welding has numerous applications across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and repair.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of welding principles and applications. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply someone interested in learning more about welding, we encourage you to continue exploring this fascinating topic. Remember to always follow proper safety precautions when working with welding equipment, and don't hesitate to reach out to us if you have any further questions or concerns.
